Web Based System
Execute daily administration tasks via a standard web browser.
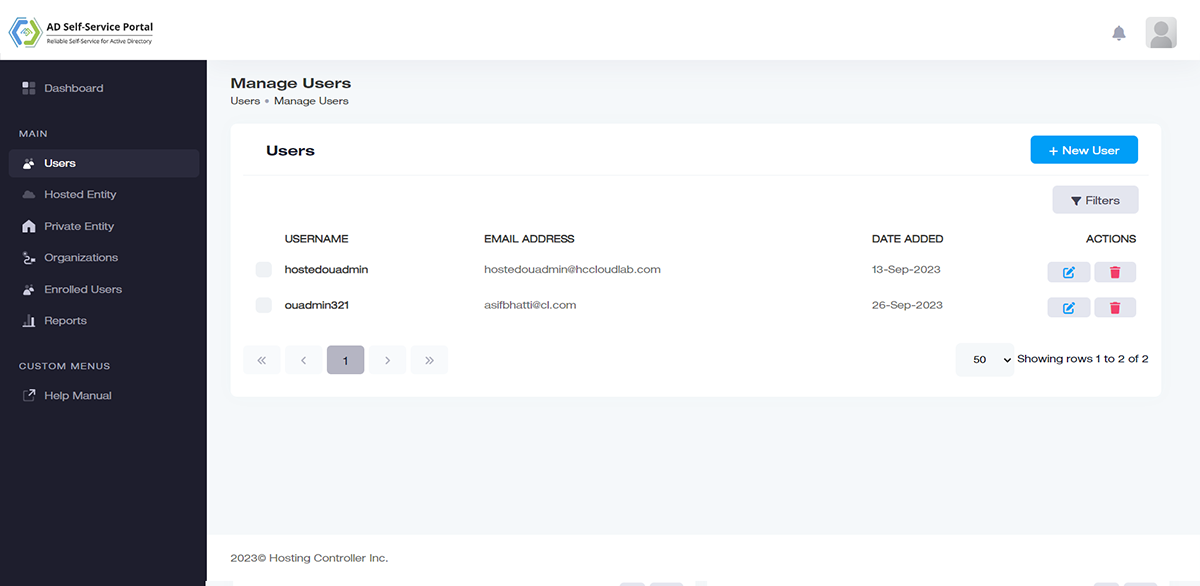
Offer Active Directory administrators and IT managers a web-based system to manage their Active Directories. Instead of employing native tools or PowerShell to provision and administer Active Directory objects, rely on the browser-accessible interface of ADSS Portal to offer absolute control of Active Directory environments.
Central Management
Control connected systems from one console.
Avoid the hassle of accessing each Active Directory separately. Manage multiple Active Directories from one central location, with a single consolidated view, be it an Active Directory in the same network as the central console or an offshore Active Directory, hundreds of miles apart.
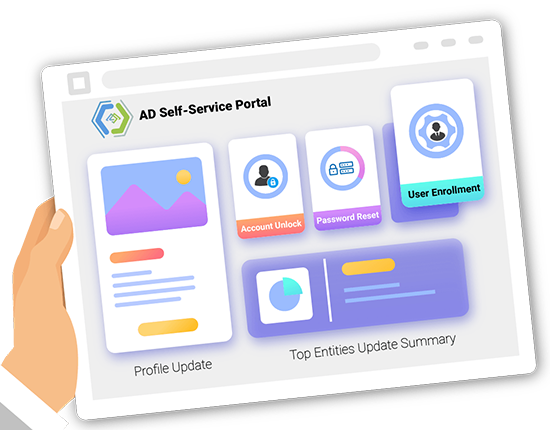
Active Directory Self-Service
Don’t let mundane tasks like password resets eat up your productive time. Allow AD users to update their own passwords, without your involvement.

Update AD Profiles
Give AD users the liberty to update their own profiles without the involvement of IT administrators.

Reset Passwords
Avoid repetitive password resets by allowing users to change their own passwords.

Unlock Accounts
Prevent users from getting locked out. Enable them to unlock their own domain accounts.
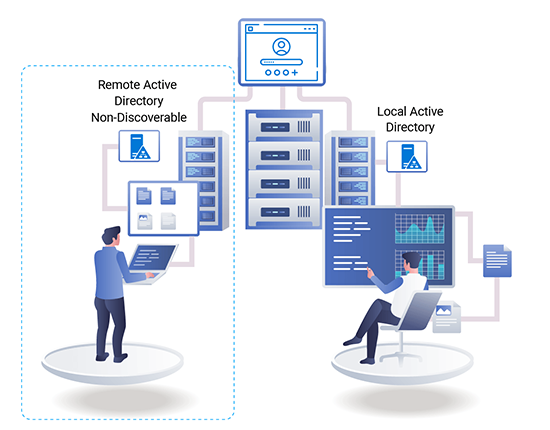
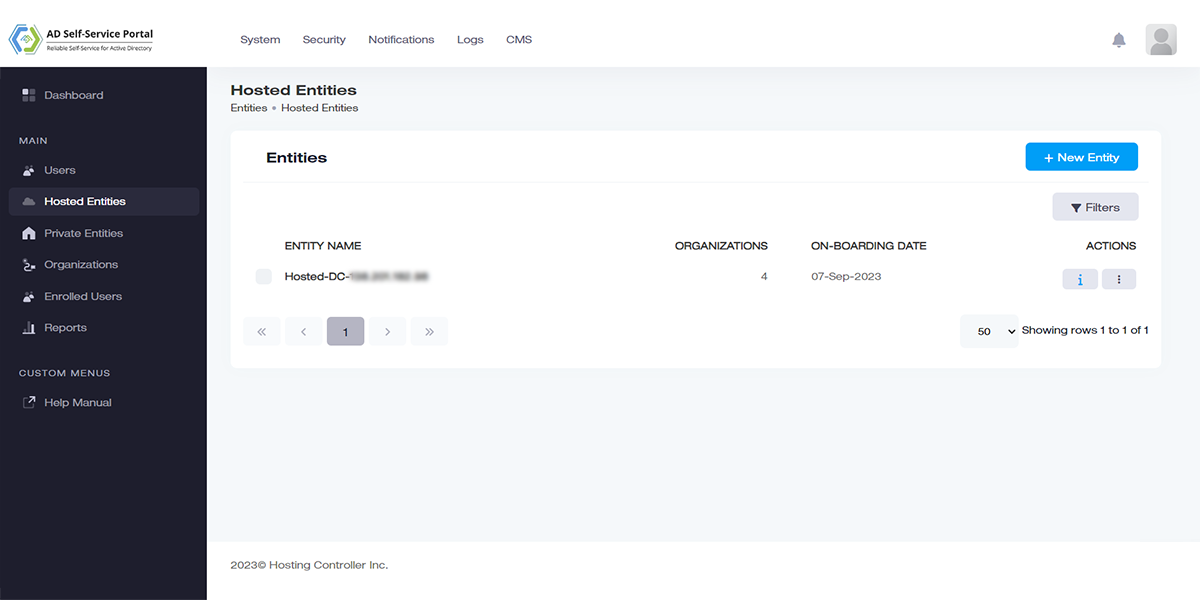
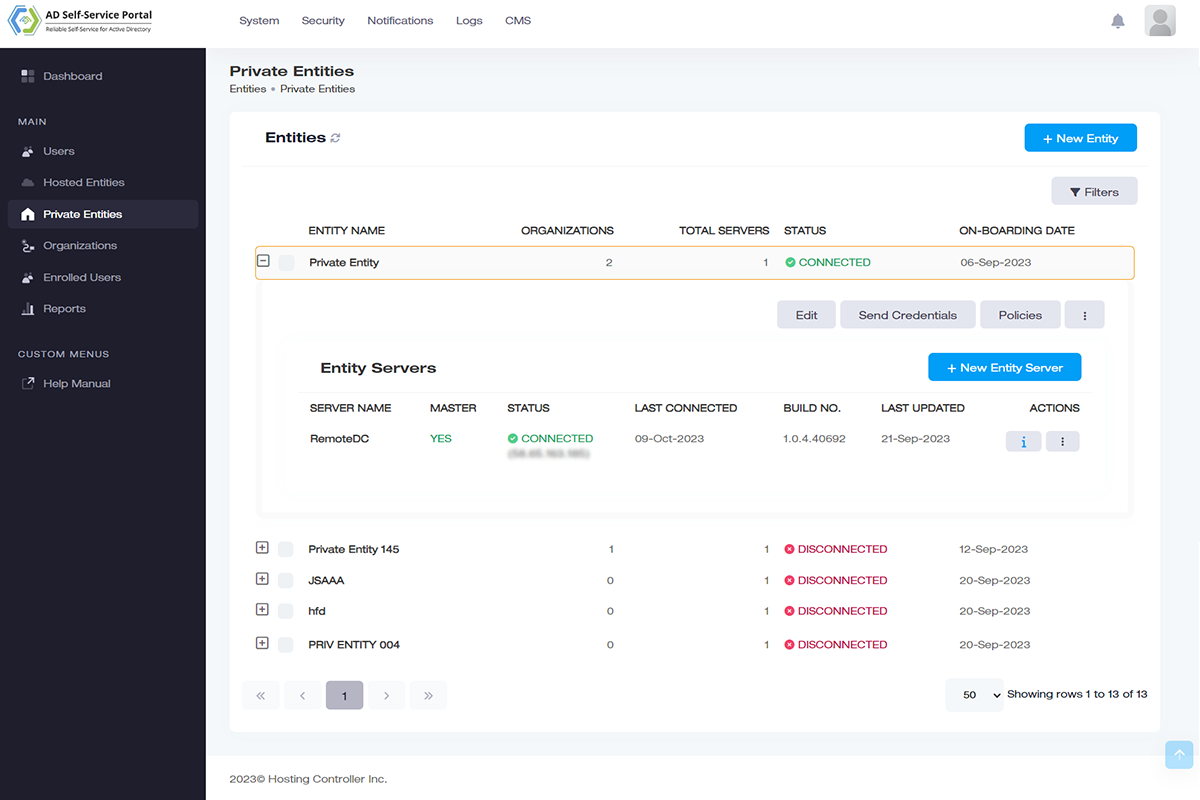
Remote Active Directories
Manage multiple Active Directories.
Manage not only local Active Directories but also multiple remote Active Directories. Remote Active Directories are ADs that are not discoverable in the network of the central console and may be distant Active Directories lying hundreds or even thousands of miles apart.
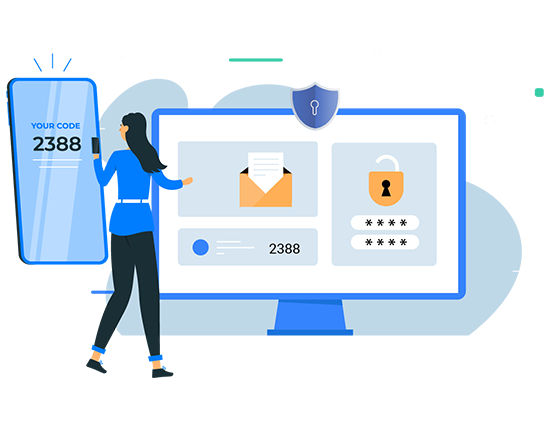
Multi-factor Authentication
Minimize security risks with MFA.
Strengthen the login process with multi-factor authentication. Allow only authenticated users to perform management actions. Ensure the delivery of one-time passwords (OTP) through email, SMS, or authenticator applications.

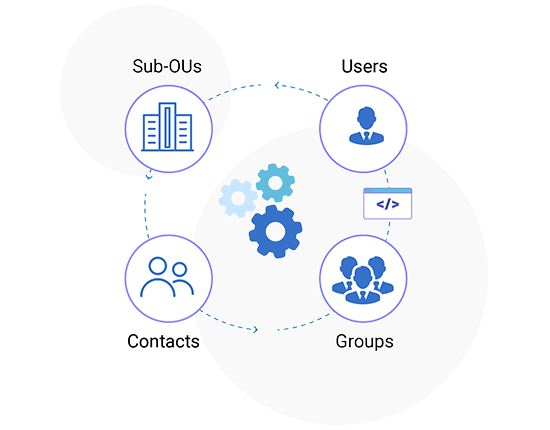
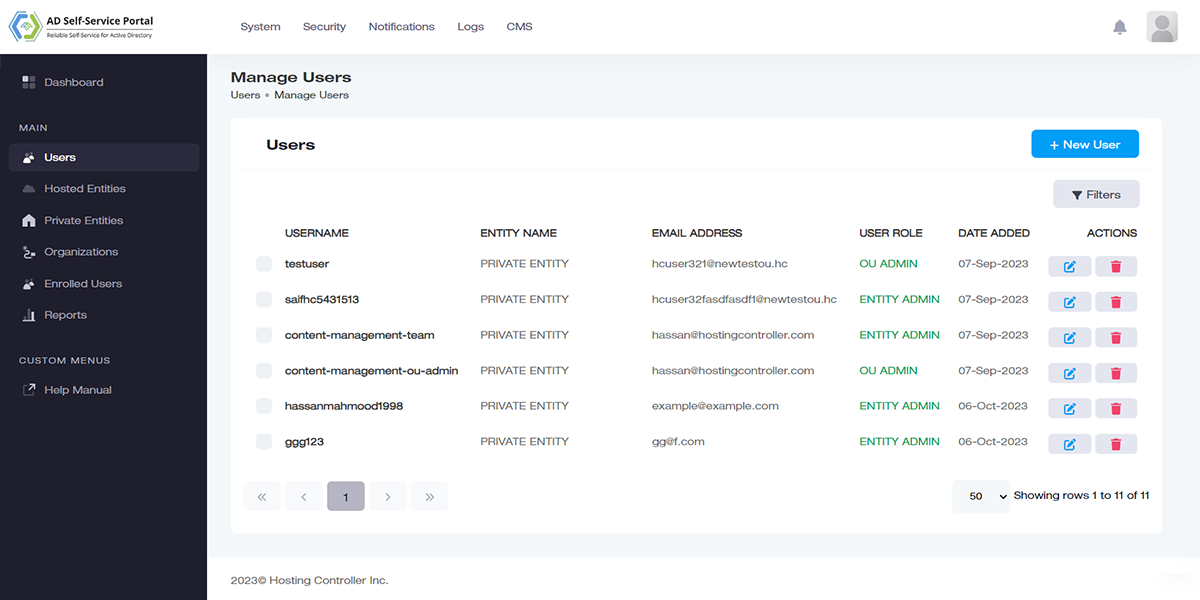
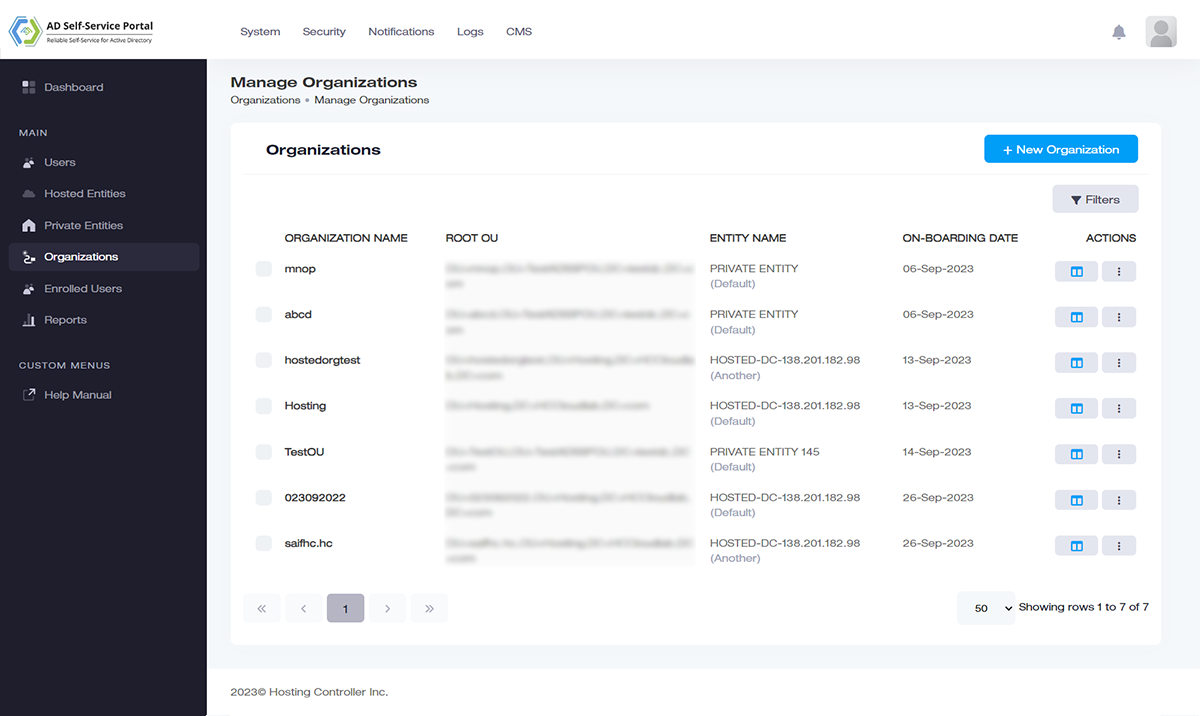
Object Provisioning
Provision directly into Active Directory.
Create AD users, groups, contacts, and sub-OUs more efficiently. Provision objects directly under organizations and even delete them if needed. Move users from one OU to another and add multiple organization suffixes to organizations.
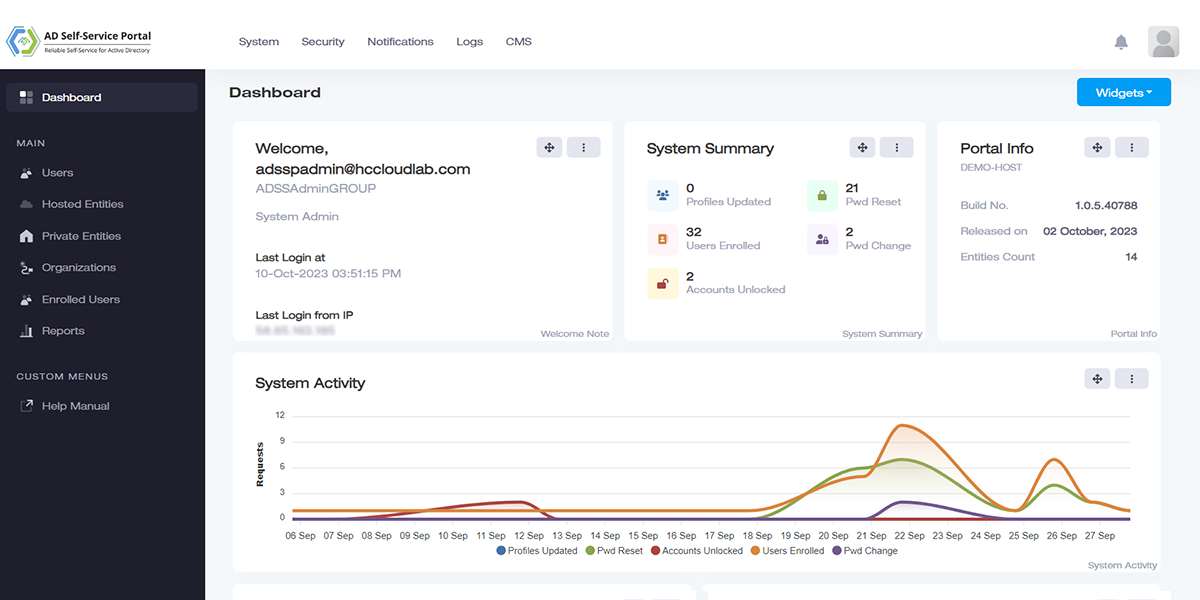
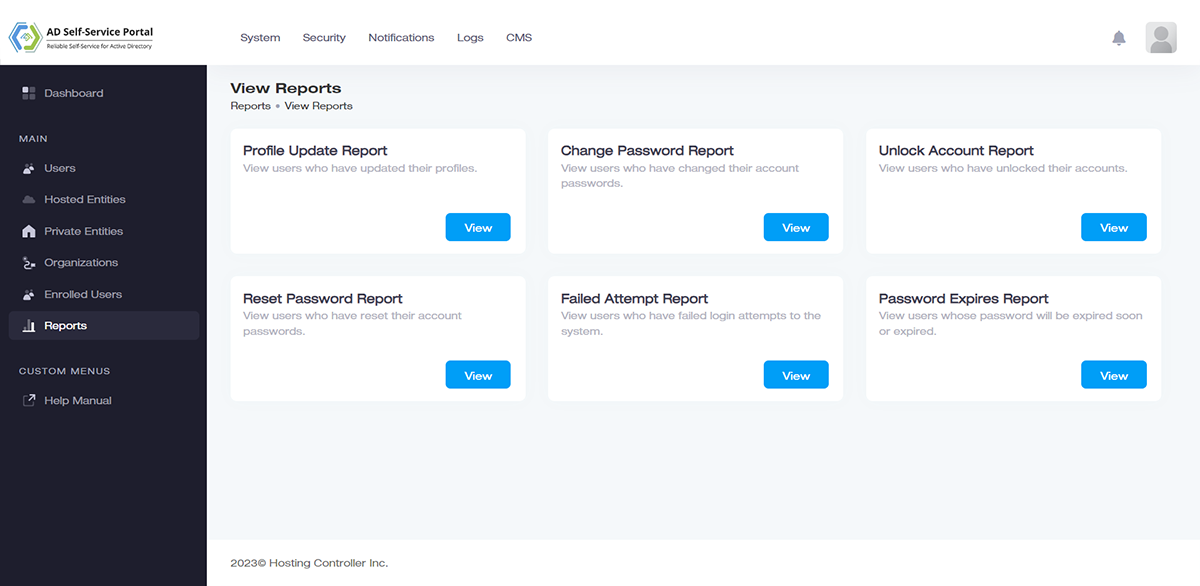
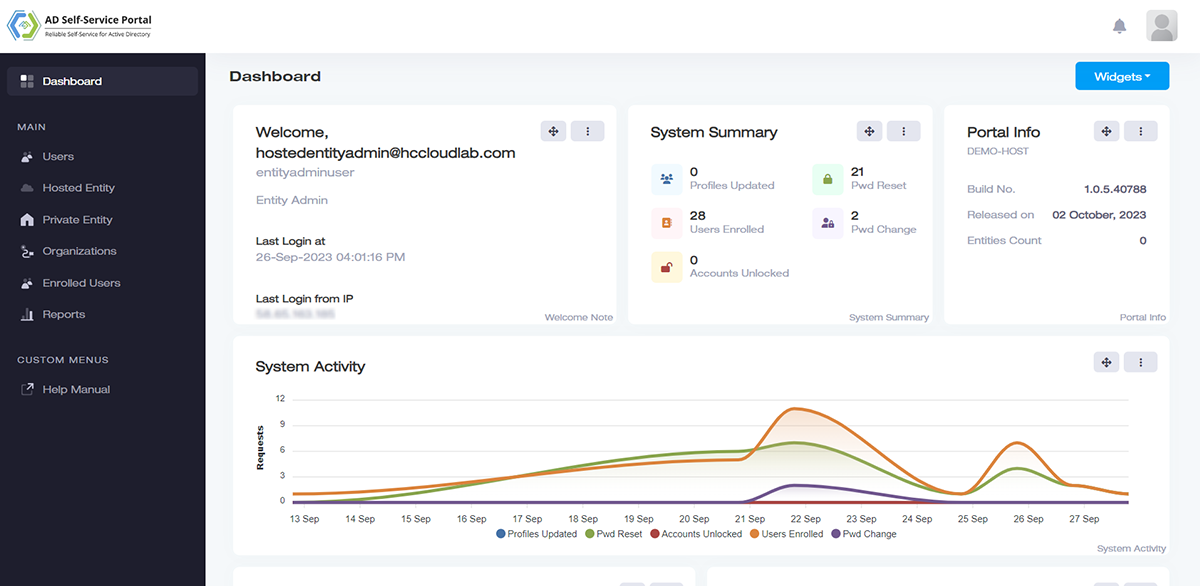
Reporting and Analytics
Monitor performance with exhaustive reports and dashboard views.
Provide complete visibility into Active Directories and glean information from various charts. See the number of profiles updated, users enrolled, passwords changed and accounts unlocked.
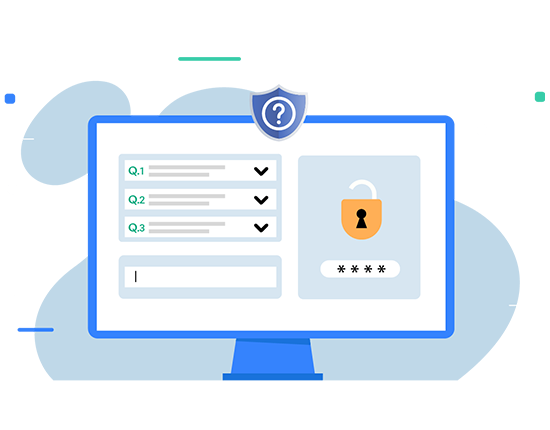

Security Questions
Ensure enrollment security through security questions.
Enroll for self-service by answering system-defined and AD-defined security questions. Thwart all login attempts that fail to answer questions correctly.
Improved Security
Enforce security through granular security checks. Restrict user access to AD data through these stringent security measures. Fend off cyber attacks.
Restrict Password Reset
Regulate password resets. Allow only a certain number of password resets a day. After the limit wait 24 hours before changing the password again.

Restrict Account Unlock
Control the number of times users can unlock their accounts in a day. After reaching the limit wait for the next day before restricting again.
Password Policy
Implement a strong password policy through complex passwords. Ensure password complexity through special characters and variable password lengths. Leverage the following Domain Controller password policy settings.

Minimum Password Length
Determine the minimum password length allowed in a password. Don’t let the password characters fall short of this length.
Alpha Characters
Define the number of alphabets to include in passwords. The password should consist of lowercase or uppercase letters.
Numeric Characters
Establish the number of numeric characters to include in passwords. The password must contain this number of digits.
Special Characters
Set the number of special characters that should accompany the password. It must contain this number of special characters.
Upper Alpha Characters
Define the number of uppercase alphabets required for the password. The password should fail if uppercase alphabets are less than this.
Go through its feature set
What can AD Self-Service Portal Do for You
Watch Video
Dive into details. Learn what ADSS portal can do for you.
Three Level Access
Separate interfaces for all admin roles.